Recycling technologies are innovative processes designed to recover materials from waste and convert them into valuable products. These technologies are crucial in many ways, including:
- Managing litter
- Conserving natural resources
- Reducing environmental pollution
- Promoting sustainable development
The importance of these technologies is becoming increasingly apparent. Our society is looking for practical solutions to manage waste and promote circularity after facing escalating environmental challenges, such as mounting waste volumes, resource scarcity, and climate change.
According to Weforum, “between 2019 and 2020, there was a 5.7% overall decrease in plastics recovered for recycling in the U.S. That is the equivalent of 290 million pounds.”
This is why recycling technologies are more than just tools for waste management. They catalyze a shift towards a more sustainable and resilient economy.
This article explores the top recycling technology trends for 2023 that will build a future where sustainability is the norm rather than the exception.
Advanced Recycling Technologies
The recycling industry is witnessing a surge in developing and adopting advanced technologies. Innovations such as smart waste bins, AI-powered sorting robots, and advanced recycling processes are increasingly prevalent.
These technologies enhance the recycling processes’ efficiency and improve the quality of recycled materials, making them more appealing to manufacturers.
For instance, CleanRobotics, a company that is revolutionizing the recycling industry with its innovative product, TrashBot. TrashBot is a smart recycling bin that uses artificial intelligence and robotics to sort waste at the point of disposal with 95% accuracy. This technology eliminates human error in waste sorting and collects data on everything that passes through the TrashBot.
Rise of Bioplastics
Bioplastics are developed from renewable resources such as:
- Corn starch
- Sugarcane
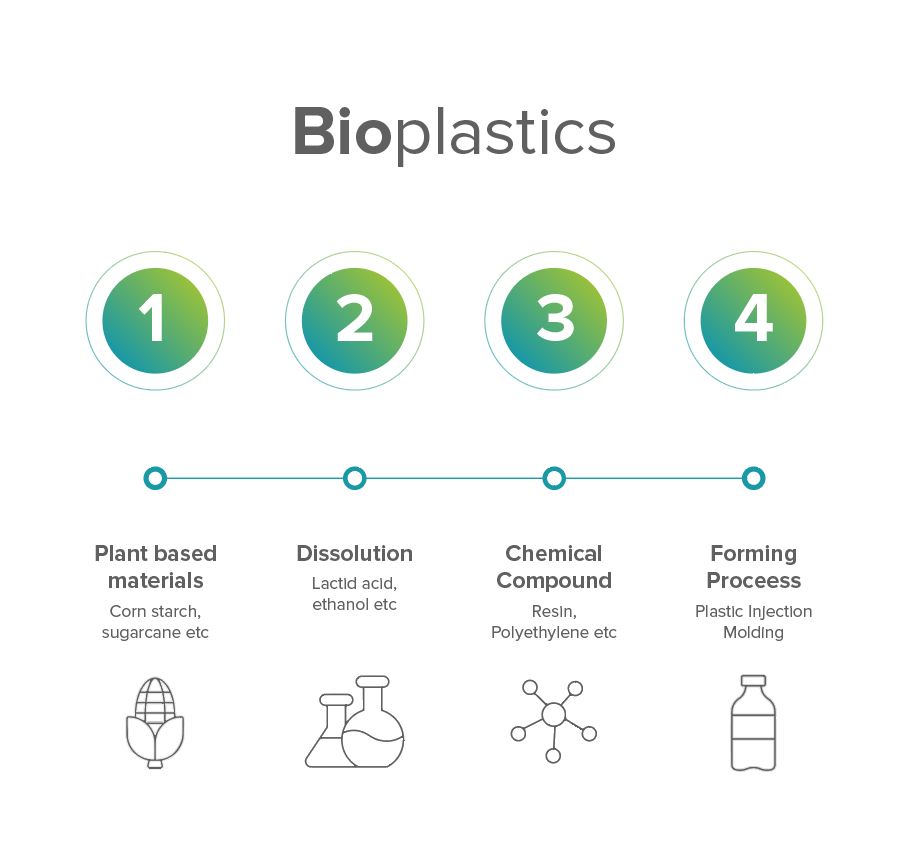
They are gaining traction as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, especially when plastic bottles take over 450 years to degrade.
These new components have enough power to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels while also decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. However, it is crucial to ensure these materials are disposed of correctly, as they require specific conditions to degrade.
A real-life example is the Italian company Novamont, which produces Mater-Bi, a type of bioplastic that is compostable and biodegradable and is used in a wide range of products, from shopping bags to coffee capsules.
Emphasis on Circular Economy
A circular economy is a utopia where businesses and governments can minimize waste and keep resources for as long as possible. This approach benefits the environment and offers economic advantages by creating new jobs and opening new markets.
IKEA, the Swedish furniture giant, is a prime example of a company embracing the circular economy. They have committed to becoming a fully circular business by 2030, which includes refurbishing and reselling used furniture, using only renewable or recycled materials, and offering a take-back service for unwanted items.
Climate Change and Sustainability
The impact of climate change is prompting a greater focus on sustainable practices, including recycling. There’s an increasing demand for materials like:
- Lithium
- Nickel
- Cobalt
- Copper
- Steel
They are essential for sustainable solutions such as zero-emission vehicles and renewable energy technologies. This trend drives the recycling industry to adapt and innovate to meet these demands.
The electric vehicle manufacturer Tesla is a key player in this trend. They have announced plans to recycle battery cells at their Gigafactory in Nevada, aiming to recover valuable metals for reuse in new batteries, reducing the need for mining and its environmental impact.
Environmental Justice
Environmental justice is the principle that everyone should enjoy the same protection from environmental and health hazards. It’s influencing recycling trends.
There’s a growing debate about exporting waste to developing nations, leading to stricter rules on waste exports and a greater focus on domestic recycling.
A significant development in this area is the Basel Convention’s amendment in 2019, which restricts plastic waste importation to developing countries. This has led to changes in global waste flows and increased domestic recycling efforts in many countries.
Plastic Recycling Innovations
Plastic remains one of the most challenging materials to recycle, but 2023 is witnessing several breakthroughs.
Chemical recycling, which breaks down plastics into their constituent parts for reuse, is gaining attention.
Companies are investing in facilities to recycle plastic waste into new products, signaling a promising future for plastic recycling.
A notable example is the partnership between Unilever and the startup Ioniqa. They use technology to break down PET plastic waste into its base molecules, which are used to create new, high-quality plastic.
Digitization and Data
Digital transformation is revolutionizing the recycling industry. From smart waste management systems to data-driven decision-making, technology is making recycling processes more efficient and effective. However, this trend also brings challenges, particularly regarding data security and privacy.
CleanRobotics, a company, is committed to the zero-waste revolution, providing innovative and cost-effective solutions for a sustainable future. Their hardware provides clean data that empowers decision-making for their clients’ zero-waste vision.
Geopolitical Realignment and Shifting Trade Patterns
As countries seek to reduce dependence on potentially hostile nations and minimize imports, there’s a greater focus on recycling domestic materials. This change is challenging but brings opportunities for the recycling industry.
The U.S.-China trade war has had significant implications for the recycling industry, with China’s ban on importing certain types of waste leading to a surge in domestic recycling efforts in the U.S. and other countries.
Dynamic Business Models
Companies prioritize resilience and self-reliance over efficiency, leading to shifts in business models. For instance, businesses are investing in recycling ecosystems to secure their supply chains, demonstrating the integral role of recycling in future business strategies.
General Motors is a prime example of this trend. They have announced plans to invest in a battery recycling ecosystem to secure the materials supply for their 100% electric vehicle production goal by 2035.
E-Waste Recycling
Recycling electronic waste, or e-waste, is another trend shaping the recycling industry in 2023. As the consumption of electronic devices continues to rise, so does the amount of e-waste generated. Statista mentions that digital scrap volume increased to 53.6 million metric tons in 2019.
Companies like ERI, a fully integrated IT company and electronics asset disposition provider, are leaders in e-waste recycling. This company is also cybersecurity-focused.
Its advanced e-waste recycling processes ensure that electronic devices are properly recycled, and any data is securely destroyed.
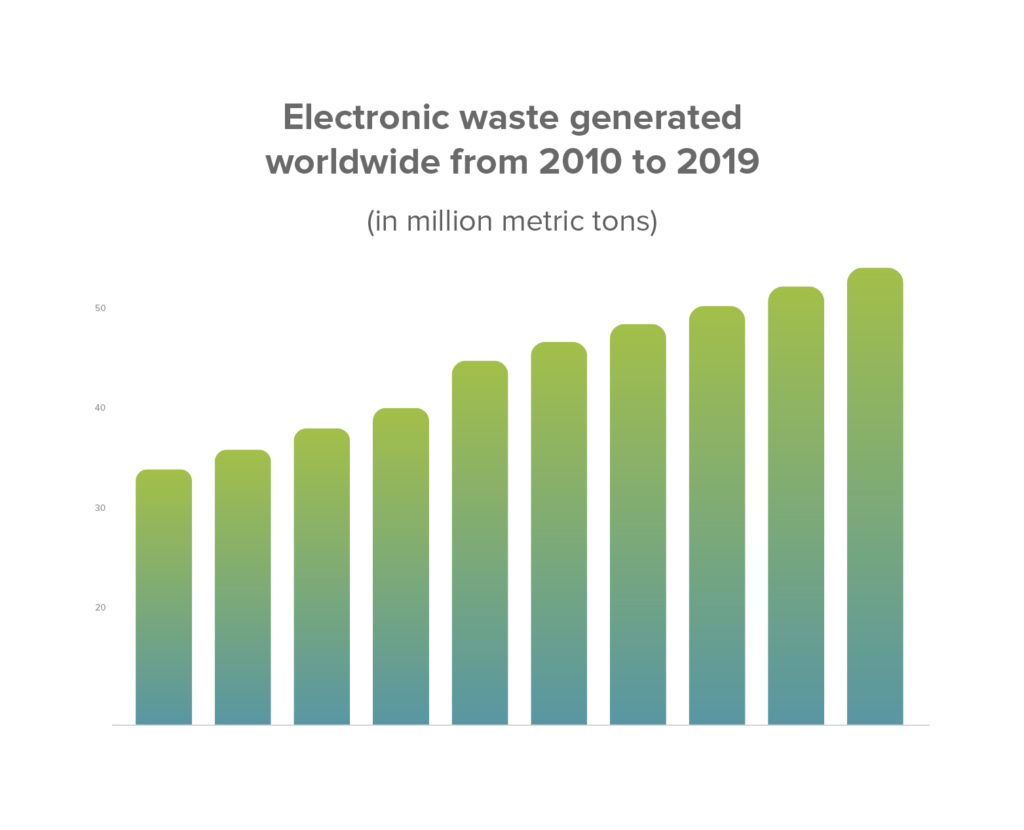
Source: Statista
Blockchain in Recycling
Blockchain technology is also making its way into the recycling industry. This technology can provide a transparent and secure way to track recyclable materials’ lifecycles, ensuring that they are properly recycled and that all parties are held accountable.
An example is the Plastic Bank, a social enterprise that has developed a blockchain-based platform for collecting and recycling plastic waste. The platform incentivizes waste collection by providing people with a secure and transparent way to exchange collected plastic for goods and services.
Since 2013, the company has collected +11 million kilograms of ocean waste.
Zero Waste Initiatives
Zero waste initiatives are becoming increasingly popular to reduce the amount of waste in landfills. These initiatives aim to redesign how we use systems and resources for product design and disposal to prevent wasteful or polluting practices. Cities, businesses, and institutions across the globe are adopting them.
For instance, San Francisco aims to reduce disposal to landfill or incineration by 61% by 2030. It has implemented a comprehensive recycling and composting program to achieve this goal.
Gitnux states, “A zero waste strategy could save 5-7% of the world’s GDP.”
Sustainable Packaging
Consumers are more and more conscious of our environmental and climatic issues. That’s why their demand for sustainable packaging options increases.
A study shows that 54% of consumers ages 44 and under consider sustainable packaging when purchasing a product.
Companies are responding by developing packaging that is easier to recycle, compostable, or reusable.
For example, Loop, a global circular shopping platform, partners with brands to offer products in durable, reusable packaging. After use, they are collected, cleaned, refilled, and reused, creating a zero-waste option for consumers.
Government Regulations
Government regulations are playing an increasingly important role in the recycling industry. These are designed to encourage recycling and reduce the amount of waste in landfills.
For example, the European Union has implemented strict waste management and recycling regulations intending to promote a circular economy. Their results have led to high recycling rates in member countries and have encouraged innovation in the recycling industry.
According to 2021 statistics, 49.6% of all municipal waste in the EU is recycled, and they are set to target 60% by 2030.
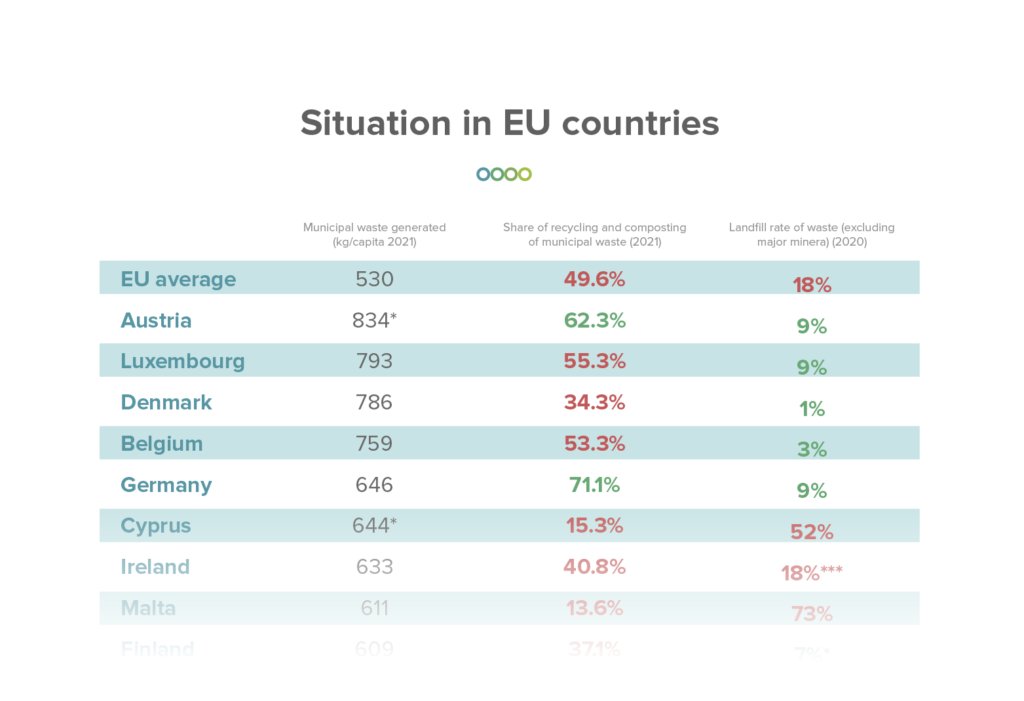
Source: Europarl
Why Are Recycling Technologies Important for The Future?
Recycling technologies are important because they help to reduce waste, conserve natural resources, save energy, mitigate climate change, and stimulate economic growth.
Let’s break down more benefits:
- Resource Conservation: Recycling technologies allow us to reuse materials, reducing the need for virgin resources. This is particularly important for non-renewable resources, such as metals and fossil fuels, which are finite and have significant environmental impacts when extracted.
- Waste Reduction: They significantly reduce the amount of waste in landfills or incinerators by turning it into valuable materials. This saves space, reduces pollution, and saves money on waste disposal costs.
- Energy Efficiency: Recycling often uses less energy than producing new materials from scratch. Recycling aluminum preserves about 95% of the energy required to produce a new element from raw materials.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Recycling reduces greenhouse gas emissions by reducing the need for extraction, manufacturing, and disposal.
- Economic Development: The recycling industry creates jobs and stimulates economic development. This includes positions in collecting, processing, and manufacturing products from recycled materials.
- Innovation and Technological Advancement: New recycling technologies drive innovation and technological advancement. This leads to more efficient and effective recycling processes, new products, and materials.
- Sustainability: They are key to achieving sustainability. Recycling allows us to use resources more efficiently and reduce our environmental impact. They are essential to building a more sustainable and resilient society.
Wrapping Up
As we look ahead to the future of recycling, it’s clear that technology plays an essential role in shaping industries. The recycling landscape is evolving rapidly from advanced sorting technologies and chemical recycling to the rise of the circular economy and the use of blockchain in tracking recyclable materials.
These trends reflect a broader shift towards sustainability in our society. As we grapple with the challenges of climate change, resource scarcity, and environmental justice, recycling technologies offer a way to reduce our environmental impact, conserve valuable resources, and build a more sustainable future.
Yet, technology alone is not the solution. Achieving our recycling goals will also require policy support, public education, and collaboration between all stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and consumers. We all have a role to play in making recycling work.
—————————-
The article was written by Oran Yehiel, Founder @ Startup Geek