In the era of environmental consciousness and heightened corporate responsibility, sustainability has become a critical concern for companies across all industries. AI systems are transforming the world and becoming an important part of our daily lives. AI is a 100 billion dollar industry and is expected to increase twenty-fold by 2030. All major sectors, like healthcare, education, retail, and marketing, are adapting AI solutions to work more efficiently. Regardless of your industry, if you want to be innovative, it’s wise to leverage the power of AI.
This article explores AI applications that are driving sustainability practices, AI’s impact on the environment, and how companies can use AI to foster a more sustainable future.
Harnessing the Power: Applications of AI in Driving Sustainability Practices
Artificial intelligence has transformed our world. There is a wide range of AI applications that are revolutionizing the way companies address environmental challenges. A 2020 study from Nature Communications shows AI can serve as an enabler for 79% of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) targets. From optimizing resource management to enabling data-driven decision-making, AI significantly drives greener business practices. Here are some typical AI applications.
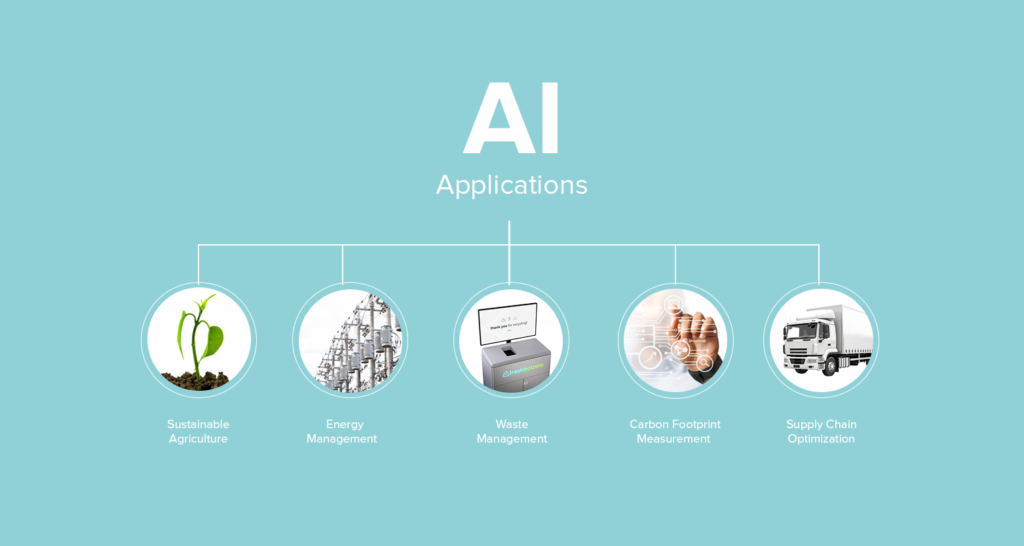
Energy Management
Clean energy and efficient energy use are essential to every sustainability initiative, and AI can help companies enhance energy efficiency in many ways. AI-powered systems can analyze real-time data on energy consumption and identify patterns to optimize energy usage. Machine learning (ML) algorithms can automatically adjust energy settings based on usage patterns, weather conditions, and occupancy levels, reducing energy waste and lowering carbon emissions. It can also encourage companies to diversify their energy sources and invest in renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Waste Management
Waste Management is an often-overlooked area that has the potential to make or break our environment. AI can optimize nearly every stage of the waste management process, from analyzing data on waste generation to sorting and collection to materials recovery facilities (MRFs). This enables companies to improve waste sorting, minimize landfill contributions, and optimize recycling and composting operations. AI-powered robots and computer vision can also enhance sorting accuracy and efficiency in recycling facilities. Even in workplaces and public facilities, smart bins like TrashBot can help reduce waste contamination by sorting accurately at the disposal point.
Supply Chain Optimization
Supply chain operation is complex, and so is making it sustainable. AI can help improve supply chain sustainability by optimizing logistics, transportation, and inventory management. AI algorithms can also analyze large datasets to identify opportunities for reducing carbon emissions, improving logistics, and minimizing packaging waste. Companies can reduce environmental impact and enhance their sustainability by auditing their supply chain operations.
Carbon Footprint Measurement
AI can accurately measure and track carbon footprints across the entire lifecycle of almost anything. Using machine learning algorithms to analyze data from various sources, companies can evaluate their energy consumption and calculate emissions. This helps identify emission hotspots, set reduction targets, and make informed decisions to mitigate an organization’s carbon footprint.
Sustainable Agriculture
AI has the potential to change the entire agricultural system. By analyzing weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop health, AI-powered systems can help agribusinesses optimize irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, reducing water waste and chemical inputs. It can also support precision farming techniques, improving yield while minimizing environmental impact. For example, a company called Carbon Robotics has created an AI-powered robot that utilizes thermal energy to target and kill weeds, cutting weed control costs for farmers by 80% and eliminating the need for toxic herbicides.
The Cost of AI-powered Sustainability: The Other Side of The Picture
Just as AI contributes to sustainability, it can also contribute to carbon emissions and climate change. The computational power required to run AI models incurs substantial environmental and financial costs. On top of the costs of hardware resources, powering that hardware also leaves a massive carbon footprint.
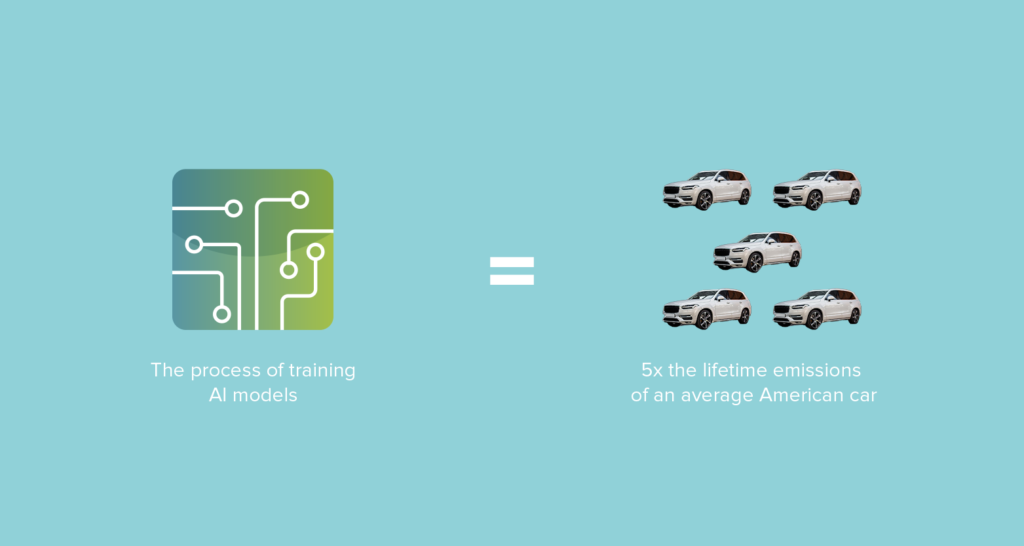
Studies have found that Google’s AlphaGo Zero – the AI that plays the game of Go against itself to self-learn – generated nearly 6 tons of carbon dioxide over 40 days of research training. That’s equivalent to almost 1000 hours of air travel. According to a paper by researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, the process of training AI models can emit more than 626,000 lbs of carbon dioxide. This is equivalent to nearly five times the lifetime emissions of an average American car (including manufacturing).
Researchers are currently working on ways to make AI more sustainable. For example, we can reduce the need for massive data by selecting only the most relevant training data or adapting existing models to new tasks. Other approaches like edge computing and neuromorphic computing can also help overcome the energy-intensive nature of current AI models and develop more sustainable AI.

Fostering a Sustainable Mindset: Empowering Companies to Embrace Sustainability
If managed well, AI is powerful and can contribute to a company’s sustainability mission. While complex and involving a multitude of disciplines, it is possible to reduce the environmental impact of AI as organizations commit to more sustainable practices.
To ensure sustainability, companies must go beyond implementing AI-driven solutions and technologies. They must develop a sustainable ethos that permeates every aspect of their operations. This way companies can empower themselves to make conscious choices that prioritize environmental stewardship and long-term sustainable operations. By embracing AI with a sustainable mindset, organizations can reimagine their impact and offer value beyond what they thought previously possible.